En

Oligonucleotides (ONs) are single-stranded or double-stranded drugs consisting of 12-30 nucleotides, including antisense oligonucleotides (ASOs), small interference RNA (siRNA) and apatmers. Their main mechanism of action is to bind to the target RNA through the principle of base complementary pairing, degrade the target RNA by endogenous nuclease, or regulate the RNA splicing and translation process through the mechanism of steric configuration blocking ribosome, so as to achieve the therapeutic purpose of the disease.
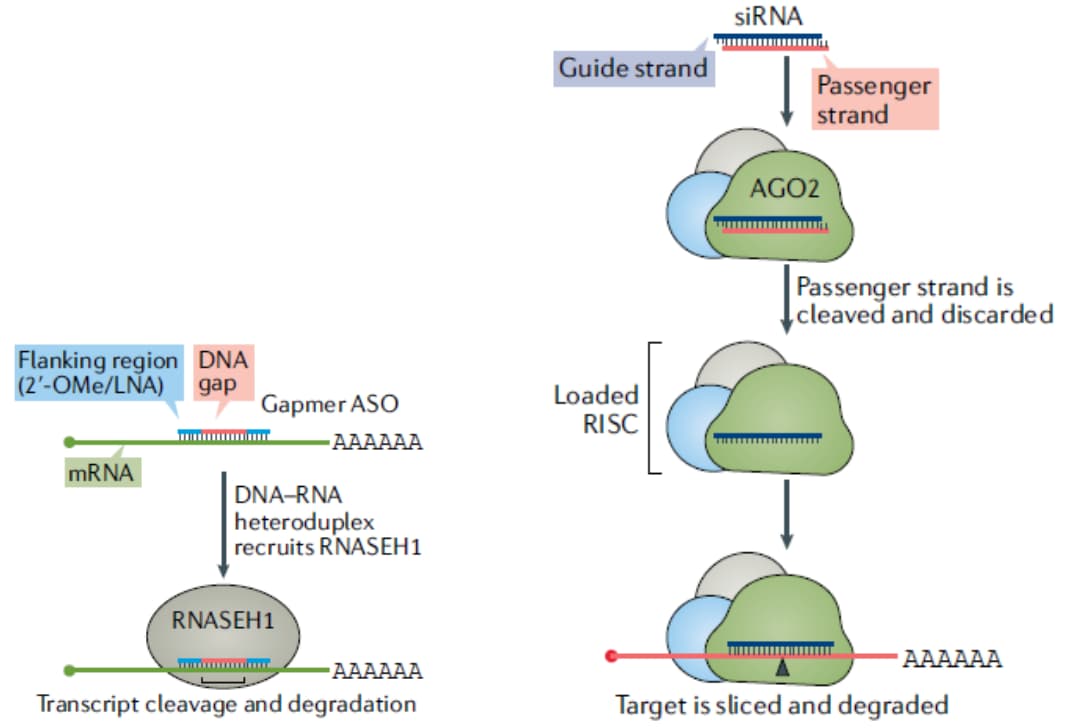
Oligonucleotide-mediated gene regulatory mechanisms
From Roberts TC et al. Advances in oligonucleotide drug delivery. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2020 Oct;19(10):673-694.
LC-MS enables precise quantitative analysis of oligonucleotides in biological samples, offering insights into base composition, sequence structure, and other essential information for metabolite identification. At INOMIXO, the quantitative analysis process of oligonucleotides in biological samples using LC-MS comprises three key steps:
Collecting in vitro incubation samples or animal plasma and tissue samples.
Pre-treating the samples through liquid-liquid extraction (LLE) or solid-phase extraction (SPE).
Conducting mass spectrometry analysis.
Call Us
Address